Hardware -




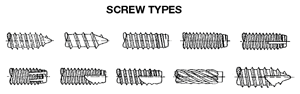
Screws and Fasteners
http://www.lelandpowell.com/bolt_types.htm
http://www.virtualforum.com/industrialhardware/
http://www.thomasregisterdirectory.com/screws/flat_head_socket_head_cap_screws_0012263_1.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bolted_joint
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Screw
Bolt Head markings
http://www.unified-eng.com/scitech/bolt/boltmarks.html
http://www.unified-eng.com/scitech/bolt/headsize.html
http://www.boltdepot.com/fastener-information/Bolt-Grade-Chart.aspx
http://www.zerofast.com/markings.htm


Types of Washers
http://www.ahc-camberley.co.uk/ti_washers.htm
http://www.machinedesign.com/BDE/FASTENING/bdefj4/bdefj4_9.html
http://www.rsrfasteners.co.uk/rsrcatalogue/pages/page27.html
http://www.astm.org/cgi-bin/SoftCart.exe/DATABASE.CART/REDLINE_PAGES/F436.htm?E+mystore
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Washer_%28mechanical%29

Nuts
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nut_%28hardware%29
Aircraft Hardware
http://www.zenithair.com/kit-data/ra/hardware.html
Rivets
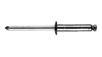

http://www.rvproject.com/rivets.html
http://www.technologystudent.com/joints/rivet1.htm
http://www.aoe.vt.edu/research/collaborative/mad/academics/projects/rivet/type.htm
http://www.zenithair.com/kit-data/ht-86-12.html
http://www.answers.com/topic/rivet
http://www.rivetsinstock.com/
Taps and Dies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taps_and_Dies#Tap
Tools
http://www.northstate.com/skilbosch/en-us/front.html
http://www.acehardware.com/sm-screwdrivers--bg-1266832.html
Sheet metal
http://blog.sylvain.trudel.com/htm/Sheet%20Metal%20Bending%20Calculator.htm
http://www.massey.ac.nz/~odiegel/bendworks/bending.pdf
http://www.solidworks.com/swexpress/pages/nov05/TT_Sheetmetal_Tips.html
http://www.me.mit.edu/Lectures/MachineTools/sheet/intro.html
http://www.precisionsheetmetal.com/home/materials.htm

Galvanic Scale
Corroded end (anodic, or least noble)
Protected end (cathodic, or most noble)
Note: Groups of metals indicate they are
closely similar in properties.
Magnesium
Magnesium alloys
Zinc
Aluminum 2S
Cadmium
Aluminum 17ST
Steel or Iron
Cast Iron
Chromium-iron (active)
Ni-Resist
18-8 Stainless (active)
18-8-3 Stainless (active)
Lead-tin solders
Lead
Tin
Nickel (active)
Inconel (active)
Brasses
Copper
Bronzes
Copper-nickel alloys
Monel
Silver solder
Nickel (passive)
Inconel (passive)
Chromium-iron (passive)
18-8 Stainless (passive)
18-8-3 Stainless (passive)
Silver
Graphite
Gold
Platinum
Reference Source: Reference Data for
Radio Engineers, Fourth Edition
Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)
Actual Size - Actual size is
the measured size of the produced
feature.
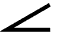
Angularity - Angularity is the
condition of a surface, axis, or center
plane, which is at a specified angle
(other than 0, 90, 180 or 270 deg.) from
a datum plane or axis.
Symbol:
Basic Dimension - A basic
dimension is a theoretically exact value
used to describe the exact size, profile,
orientation or location of a feature. A
basic dimension is always associated with
a feature control frame or datum target.
Block tolerance does not apply and the
applicable tolerance will be given to the
feature control frame. Basic dimensions
are enclosed by a rectangle.
Symbol:

Bilateral Tolerance - A
bilateral tolerance is a tolerance in
which variation is permitted in both
directions from a specified dimension
(example +- .005).
Center Plane - Center plane is
the middle or median plane of feature.
Circularity - See Roundness.
Clearance Fit - A clearance fit
is one having limits of size defined such
that a clearance always results when
mating parts are assembled.
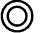
Concentricity - Concentricity
describes a condition in which two or
more features (cylinders, cones, spheres,
etc.) In any combination have a common
axis. Measurement requirements for
concentricity involves the complex task
of mapping the referenced feature by way
of opposed point measurements. A through
understanding of the measurement process
should be investigated before defining
feature relationships using
concentricity.
Symbol:
Coaxial - Coaxial describes a
condition where two or more features have
the same axis or centerline.
Coordinate Dimension - (1)
Either of two coordinates that locate a
point on a plane and measured its
distance from either of two intersecting
straight-line axes along a line parallel
to the other axis. (2) Any of three
coordinates that locate that locate a
point in space and measure its distance
from any of three intersecting coordinate
planes measured to that one of three
straight-line axes that is the
intersection of the other two planes.
Coplanar - Coplanar describes a
condition of two or more surfaces having
all elements in the same plane.
Cylindricity - Cylindricity
describes a condition of a surface of
revolution in which all points of a
surface are equidistant from a common
axis.
Symbol:
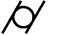
Datum - Datums are points,
lines, planes, cylinders, axes, etc., a,
from which the location, or geometric
relationship of other part features may
be established or related.
Datum Axis - the datum axis is
the theoretically exact centerline of the
datum cylinder as established by the
extremities or contacting points of the
actual datum feature cylindrical surface,
or the axis formed at the intersection of
two datum planes.
Datum Feature - A datum feature
is the actual component feature used to
establish a datum.
Datum Identification frame
(Symbol) - The datum identification frame
(symbol) contains the datum reference
letter in a rectangular box, usually
preceded and followed by a dash (any
letter except I, O, or Q).
Datum Line - A datum line is
that which has length but no breadth or
depth, such as, an intersection line of
two planes, centerline or axis of holes
or cylinders and/or reference line for
functional tooling or gauging purposes.
Datum Point - A datum point is
that which has position, but no extent;
such as, the apex of a pyramid or cone,
center point of a sphere or reference
point on a surface for functional tooling
or gauging purposes.
Datum Reference - A datum
reference is a datum feature.
Datum Reference Plane - is a
set of three mutually perpendicular datum
planes or axis established from the
simulated datum in contact with datum
surfaces or features and used as a basis
for dimensions for designs, manufacture,
and inspection measurement.
Datum Simulator - A datum
simulator a surface of adequate precision
oriented to the high points of a
designated datum from which the simulated
datum is established. Examples: gage
pin, block, surface of granite block.
Diameter Symbol - the diameter
symbol, indicates a circular feature when
used on the field of a drawing or
indicates that the tolerance is
diametrical when used in a feature
control frame.
Datum Target - is a specified
point, line, or area on a part that is
used to establish the Datum Reference
Plane for manufacturing and inspection
operations.
Dimension - A dimension is a
numerical value expressed in appropriate
units of measure and indicated on a
drawing.
Feature - Features are specific
component portions of a part and may
include one or more surfaces, such, as
holes, screw threads, profiles, faces or
slots. Features may be individual or
interrelated.
Feature Of Size - One
cylindrical or spherical surface, or a
set of two plane parallel surfaces, each
of which is associated with a size
dimension.
Feature Control frame (Symbol)
- The feature control frame symbol is a
rectangular box containing the geometric
characteristics symbol, and the form,
runout or location tolerance. If
necessary, datum references and modifiers
applicable to the feature or the datums
are also contained in the box.
Fit - Fit is a general term
used to signify the range of tightness or
looseness, which may result from the
application of a specific combination of
allowances and tolerance in the design of
mating part features. Fits are four
general types: interference, transition,
line and clearance.
Flatness - Flatness is the condition
of a surface having all elements in one
plane.
Symbol:
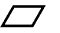
Form Tolerance - A form
tolerance states how far an actual
surface of feature is permitted to vary
from desired form the desired form
implied by the drawing. Expressions of
these tolerances refer to flatness,
straightness, parallelism,
perpendicularly, angularity, roundness,
cylindricity, profile of a surface and
profile of a line.
Free State Variations - Free
state variation is a term used to
describe distortion of a part after
removal of forces applied during
manufacture.
Geometric Characteristics -
Geometric characteristics refer to the
basic elements or building blocks, which
form the language of geometric
dimensioning and tolerancing. Generally,
the term refers to all the symbols used
in form, runout, and locational
tolerancing.
Geometric Tolerance - The
general term applied to the category of
tolerances used to control form, profile,
orientation, location, and runout.
Implied Datum - An implied
datum is an unspecified datum whose
influence on the application is implied
by the dimensional arrangement on the
drawing; example, Coordinate dimensioning
is applied to part, the zero dimension is
attached to a feature this feature is
implied as a datum element; axis,
surface or plane.
Interference Fit - An
interference fit is one having limits of
size so prescribed that an interference
always results when mating parts are
assembled.
Least Material Condition - (LMC)
- This term implies that condition of a
part feature of size wherein it contains
the least (minimum) amount of material,
examples, largest hole size and smallest
shaft size. It is opposite to maximum
material condition (MMC).
Symbol:

Limit Dimensions - In limit
dimensioning only the maximum and minimum
dimensions are specified. When used with
dimension lines, the high limit is placed
over the low limit. When used with a
leader line or note, the low limit
precedes the high limit.
Limits Of Size - The specified
maximum and minimum size of a given
feature.
Limits of Size Concept - The
limits of size concept calls for perfect
form at maximum material condition. Also
called the Taylor principle.
Line to Line Fit - A line fit
is one having limits of size so
prescribed that surface contact or
clearance may result when mating parts as
assembled.
Location Tolerance - A
tolerance states how far an actual
feature may vary from the perfect
location implied by the drawing as
related to datums or other features.
Expressions of these tolerances refer to
the category of geometric characteristics
containing position, concentricity, and
symmetry.
Maximum Material Condition - (MMC)
Maximum material condition is that
condition of a part feature wherein it
contains the maximum amount of material
within the stated limits of size. That
is: minimum hole size and maximum shaft
size.
Symbol:

Modifier - A modifier is the
term used to describe the application of
geometric principles. The principles
include MMC, LMC, RFS, projected
tolerance zone and diameter.
Nominal Size - The nominal size
is that stated designation which is used
for the purpose of general
identification, examples: 1.400, .050 .
Parallelism - Parallelism is
the condition of a surface, line, or
axis, which is equidistant at all, points
from a datum plane or axis.
Symbol:

Perpendicularity -
Perpendicularity is the condition of a
surface, axis, or line, which is 90 deg.
From a datum plane or a datum axis.
Symbol:
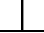
Position Tolerance - Position
tolerance (formerly called true position
tolerance) defines a zone within which
the axis or center plane of a feature is
permitted to vary from true
(theoretically exact) position.
Symbol:

Principle Of Independency -
This principle sets no limits to the
number of errors of form possessed by
individual features of a work piece.
International designer, except the USA,
use this principle.
Profile Of A Line - Profile of
a line is the condition permitting a
uniform amount of profile variation,
ether unilaterally or bilaterally, along
a line element of a feature.
Symbol:

Profile Of A Surface - Profile
of a surface is the condition permitting
a uniform amount of profile variation,
ether unilaterally or bilaterally, on a
surface.
Symbol:

Projected Tolerance Zone - A
projected tolerance zone applies to a
hole in which a pin, stud, screw, etc.,
is to be inserted. It controls the
perpendicularity of the hole to the
extent of the projection from the hole
and as it relates to the mating part
clearance. The projected tolerance zone
extends above the surface of the part to
the functional length of the pin, stud,
and screw relative to its assembly with
the mating part.
Symbol:

Reference Dimension - A
dimension, usually without tolerance,
used for information purposes only. It
does not govern production or inspection
operations. A reference dimension is a
repeat of a dimension or is derived from
other values on the drawing or related
drawings. Symbology: (.250)
Regardless Of Feature Size - (RFS)
- This is the condition where the
tolerance of form, runout or location
must be met irrespective of where the
feature lies within its size tolerance.
Optional for Position.
Symbol:

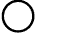
Roundness - Roundness describes
the condition on a surface of revolution
(cylinder, cone, sphere) where all points
of the surface intersected by any plane
(1) perpendicular to a common axis
(cylinder, cone), or (2) passing through
a common center (sphere) are equidistant
from the center.
Symbol:
Runout - Runout is the
composite deviation from the desired form
of a part surface of revolution through
on full rotation (360 deg) of the part on
a datum axis.
Symbol:
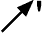
Runout Tolerance - Runout
tolerance states how far an actual
surface of feature is permitted to
deviate from the desired form implied by
the drawing during one full rotation of
the part on a datum axis. There are two
types of runout: circular runout and
total runout.
Size Tolerance - A size
tolerance states how far individual
features may vary from the desired size.
Size tolerances are specified with ether
unilateral, bilateral or limit tolerance
methods.
Specified Datum - A specified
datum is a surface or feature identified
with a datum identification symbol of
note.
Squareness - See Perpendicularity.
Straightness - Straightness
describes a condition where an element of
a surface or an axis is a straight line.
Symbol:
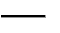
Symmetry - Symmetry is a
condition in which a feature (or
features) is symmetrically disposed about
the center plane of a datum feature.
Tolerance - A tolerance is the
total amount by which a specific
dimension may vary; thus, the tolerance
is the difference between the maximum and
minimum limits.
Transition Fit - A transition
fit is one having limits of size so
prescribed that either a clearance or an
interference mat result when mating parts
as assembled.
True Position - True position
is the theoretically exact location of a
feature established by basic dimensions,
also referred to as "Position or
positional tolerance"
Symbol:

Total Runout - Total runout is
the simultaneous composite control of all
elements of a surface at all circular and
profile measuring positions as the part
is rotated through 360.
Symbol:
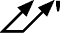
Unilateral Tolerance - A
unilateral tolerance is a tolerance in
which variation is permitted only in one
direction from the specified dimension,
example, 1.400 +.000/ -.006.
Virtual Condition (Size) - The
boundary generated by the collective
effects of MMC, size limit of a feature
and any associated geometric tolerance,
virtual condition must be considered in
determining the fit between mating parts.
The term "virtual condition" is preferred
over "virtual size."
More to come...



