Acronyms - There are so many
acronyms in electronics... here is a good
site to look up acronyms
http://www.acronymfinder.com/
AWG—American
Wire Gauge formerly known as the Brown
and Sharpe (B + S) Gauge. The gauge is
calculated so that the next largest
diameter always has a cross-sectional
area that is 26% greater.
ASTM—American
Society of Testing and Materials.
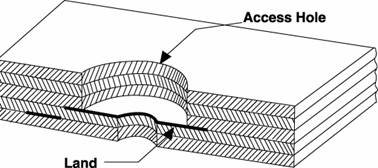
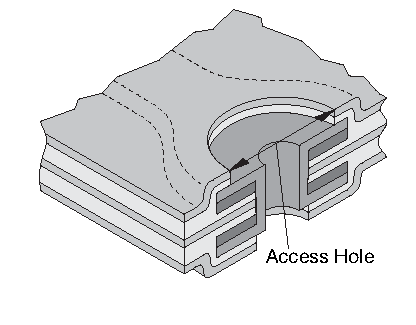
Access Hole, Inner Pad - A series
of larger diameter holes in successive
upper layers of a multilayer printed
circuit board such that each of the holes
has its center on the same central axis
and the main hole in the board. These
open relief areas provide access to the
surface of the internal copper land on an
inner layer of the pc board for testing
or attachment. Sometimes used to insulate
the bottom pad of a board from a
conductive mounting surface.
AC or Alternating
Current
There are two types of electrical
currents in electronics, Direct
Current and Alternating Current. AC
and DC are descriptive labels
referring to the electron flow
patterns in a conductor verses time.
First the flow may be positive in
voltage then it changes to negative
voltage causing current to flow in
alternating directions in the
conductor. Direct current is typically
a steady state voltage that mimics the
pattern seen when a battery cell is
attached to a complete circuit with
current flowing in only one direction.
AC is an alternating current that
varies with time allowing the electron
current to flow in both directions along
the conductor at a fixed or variable
rate, switching polarity many
times per second. Some common types of
waveforms associated with alternating
currents when viewed using an
oscilloscope will take the shape of a
sinusoidal, square wave , or
triangular and saw tooth wave pattern.
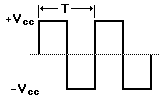
Square Wave
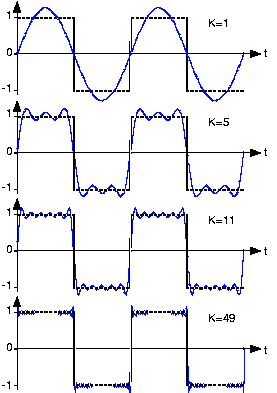
Approximating the
square wave
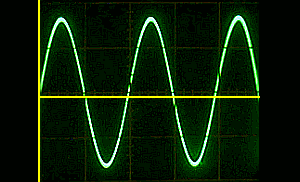
Sine wave

Triangular wave
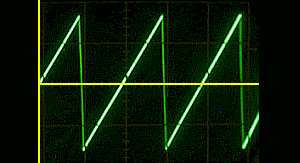
Saw tooth wave
Ambient
Typically the average air temperature
surrounding the heat source or system
that must have a path for component
heat flow to cool the unit under test.
Under electronic test conditions the
ambient temperature that the unit may
be exposed to must be artificially
raised and lowered to the maximum
temperatures that the unit under test
would be exposed to in normal use.
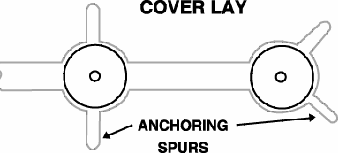
Anchoring Spur
An extension of a land on a flexible
printed board that extends beneath the
cover lay to assist in holding the
land to the base material typically
used for Flex Circuits between the
layers of Kapton to reinforce the pad
structure.